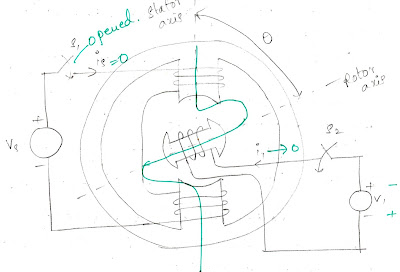
Classification of surveying:
Definition of Surveying:
It is defined as an art to determine the relative positions of points on, above or beneath the surface of the earth, with respect to each other, by measurements of horizontal and vertical distances, angles and directions.
It is defined as an art to determine the relative positions of points on, above or beneath the surface of the earth, with respect to each other, by measurements of horizontal and vertical distances, angles and directions.
Classification of surveying based on Accuracy:
1. Plane Surveying
Survey in which the mean surface of earth is regarded as plane surface and not curved as it really is, known as plane surveying. Following assumptions are made in this surveying.
- The error introduced for a length of an arc of 18.5 km is only 0.0152m greater than the subtended chord. The difference between the sum of the angles of spherical triangle and that of plane triangle is only one.
- Plane surveys are done for engineering projects on large scale such as factories, bridges, dams, location and construction of canals, highways, railways etc, and also for establishing boundaries.
2. Geodetic Surveying
Survey in which the shape of the earth's surface is taken into account and a higher degree of precision is exercised in linear and angular measurements is termed as geodetic surveying. Such surveys extend over large area.
Classification of surveying based on Instrument:
1. Chain Survey
When a plane is to be made for very small open field, the field work may consist of linear measurements only. All the measurements are done with a chain and tape. It is recommended for plans involving the development of buildings, roads, water supply and sewerage schemes.
2. Transverse Survey
When the linear measurements are done with chain and tape and the directions or angles are measured with compass or transit theodolite respectively is called traversing survey. In traversing speed and accuracy of the field work is enhanced. A traverse survey is useful for large projects such as reservoirs and dams.
3. Tacheometry
This method of surveying in which both the horizontal and vertical distances are determined by observing a graduated staff with a transit theodolite equipped with a special telescope having stadia wires and anallatic lens. It is very useful when the direct measurements of horizontal distances are inaccessible. It is usually recommended for making contour plans of building estates, reservoirs etc.
4. Levelling
This is a method of surveying in which the relative vertical heights of the points are determined by employing a level and a graduated staff.
5. Plane tabling
It is a graphical method of surveying in which field work and plotting are done simultaneously. A clinometer is used in conjuction with plane table to plot the contours of the area and for filling in the details.
6. Triangulation
When the area to be surveyed is of considerable extent, triangulation is adopted. The entire area is divided in a network of triangles.
Classification of surveying based on Purpose :
1. Engineering Survey
Surveys which are done to provide sufficient data for the design of engineering projects such as highways, railways, water, supply, sewage disposal, reservoirs, bridges etc.
2. Construction Survey
It consists of topographic survey of the area, measurement of earth work, providing grade, and making measurement of the complete work till date.
3. Geological Survey
In this survey both the surface and sub surface is required to determine the location, extent and reserves of different minerals and rock types. Geoological structures like folds, faults and unconformities may help to locate the possibility of the occurance of economic minerals, oils etc.
4. Geographical Survey
Surveys conducted to provide sufficient data for preparation of geographical maps.
5. Mine Survey
In this surveying both surface and underground are required.
6. Reconnaissance Survey
A visit is made to the site and all the relevant information is collected. It includes collection of existing maps of the area, tracing the relevant map portion over a paper, incorporating the details of the area, if missing, by conducting round survey.
Classification of surveying based on Place
1. Land Survey
It consists of rerunning old land lines to determine their lengths and directions.
2. Topographical Survey
This is a survey conducted to obtain data to make a map indicating inequalities of land surface by measuring elevations and to locate the neutral and artificial features of the earth.
3. Cadastral Survey
This is referred to extensive urban and rural surveys made to plot the details such as boundaries of fields, houses and property lines. These are also known as public end surveys.
4. Hydrographic Survey
it deals with the survey of water bodies like streams, lakes, coastal waters, and consists in acquiring data to chart the shore lines of water bodies.
You may also like to view:
3. Error due to use of wrong scale in surveying
4. Error in computed results in surveying
5. Problems on Surveying
5. Problems on Surveying